

Mathematics is an evolving discipline. It is constantly expanding and changing. Although the ancient Greeks, for instance, began to develop number theory and made major contributions to geometry and logic, they had little inkling of probability, which wasn't formalized until the mid 1600s.
|
| 3000 B.c | Egyptians and Babylonians begin the development of number systems and early bookkeeping. Simple problems of arithmetic and geometry necessary to a civilized society become commonplace. |    |
| 700 B.c. | Ancient Greece starts to flourish. Greek thinkers contribute number theory, geometry, and logic to mathematics. |  |
| 530 B.c | Pythagoras, one of the most famous of the Greek mathematicians and philosophers, founds the Pythagorean movement. |   |
| 300 B.c. | Euclid completes his writing of Elements, 13 volumes on mathematics. |   |
| 100 A.D | Astronomers begin to develop trigonometry. |  |
| 170 | Ptolemy, mathematician and astronomer, declares that the earth is the center of the universe. This becomes the dominate view until the 17th century when Copernicus claims that the sun is the center of the solar system. |  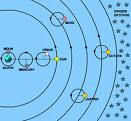 |
| 200 | Diophantus, a Gr~ek mathematician, develops algebra. He is considered by many to be the father of that subject. |  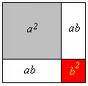 |
| 540 | Diophantus and astronomer, advances mathematics by solving the quadratic equation. |   |
| 600 | Geometry, algebra, and numeral systems benefit from Hindu and Arabian thought. The idea of zero is introduced |   |
| 775 | The translation of Hindu mathematics to Arabic takes place. | |
| 830 | al-Khowarizml, an Arabian, works with algebra, numeral systems, and equations. |  |
| 1100 | Arabic and Hindu mathematics spread throughout Western Europe. |  |
| 1200 | Leonardo of Pis a (Fibonacci), an Italian, works with equations, sequences, series, and Pi. | .  |
| 1478 | The first mathematics books are printed. |  |
| 1489 | The signs of + and - are introduced |  |
| 1500 | Negative numbers and perspective are introduced. |  |
| 1525 | Great work is done on solving equations. |  |
| 1540 | Imaginary numbers are explored. |  |
| 1557 | Englishman Robert Record writes the first English algebra text. |  |
| 1560 | The Italian Girolamo Cardano works with complex numbers, equations, and probability. |  |
| 1580 | Decimals are introduced. |
  |
| 1614 | John Napier, Scottish mathematician, creates the first system of logarithms. He is the first to use the decimal point. |    |
| 1630 | The coordinate system is developed. |  |
| 1640 | Rene Descartes, French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, works on systemizing analytic geometry. He also attempts to classify curves according to the types of equations that produce them. |   |
| 1645 | Pierre de Fermat, French mathematician, studies various topics, including coordinates, polygons, probability, and the Pythagorean theorem. |   |
| 1650 | Blaise Pascal, French philosopher, physicist, and mathematician, formulates one of the basic theorems of projective geometry, known as Pascal's theorem. He also invents the first adding machine. |   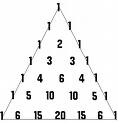 |
| 1680 | The German Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz works on calculus, functions, and infinity. |    |
| 1700 | Work on determinants is done. |  |
| 1780 | Complex numbers are explored by several mathematicians. |   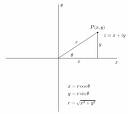 |
| 1799 | The Metric System is introduced. |   |
| 1800 | Theories on projection are developed. Number theory is explored. |  |
| 1810 | Carl Friedrich Gauss, a German mathematician, expands the study of number theory. |   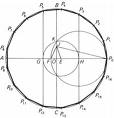 |
| 1820 | The Russian Nikolai Ivanovich LCl'Qachevsky works on geometry. |  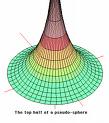 |
| 1840 | Various mathematicians work with matrices, vectors, and symbolic logic. |     |
| 1870 | George Cantor works with infinite sets. |   |
| 1905 | Albert Einstein develops the theory of relativity. |   |
| 1910 | Various mathematicians, including Alfred North Whitehead and Bertrand Russell, study the logical foundations of mathematics. |    |
| 1920 | Emmy Noether studies abstract algebra. |   |
| 1945 | Various mathematicians and researchers work on computers. |   |
| 1976 | Kenneth Appel and Wolfgang Haken find a solution of the Four Color Problem. |    |
| 1977 | Robert Connelly finds a rigidity counterexample. |  |
| 1993 | Andrew Wiles presents what he believes is the proof of the most famous problem in mathematics-Fermat's last theorem. At the time of this book's printing, Wiles' work has not been confirmed. |  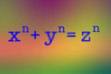  |
The Math Teacher's Book of Lists 1995 by Prentice Hall
